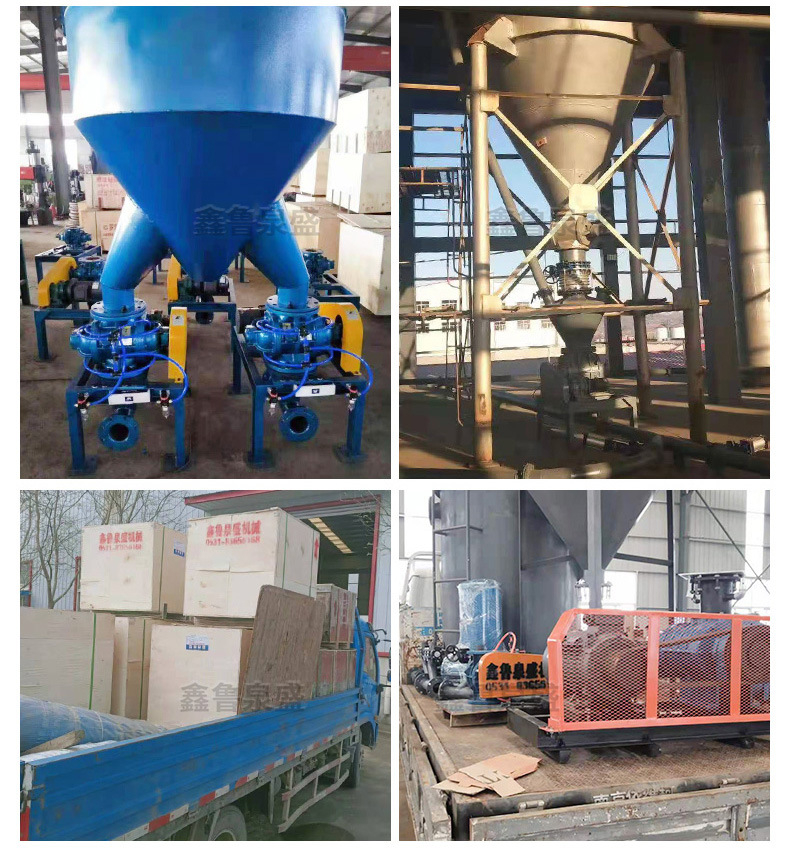
The rotary feeder is easy to suck in materials under negative pressure, so the feeding at the throat is simple. The material is easy to evaporate when transported under negative pressure, making it easier to transport materials with higher moisture content than the pressure feeding type. It can also cool the materials supplied under heating conditions. The components need to be sealed, such as the separator, dust collector, and air lock. The structure of the components is relatively complex, and the fan is located at the end of the system, requiring a high degree of air purification.
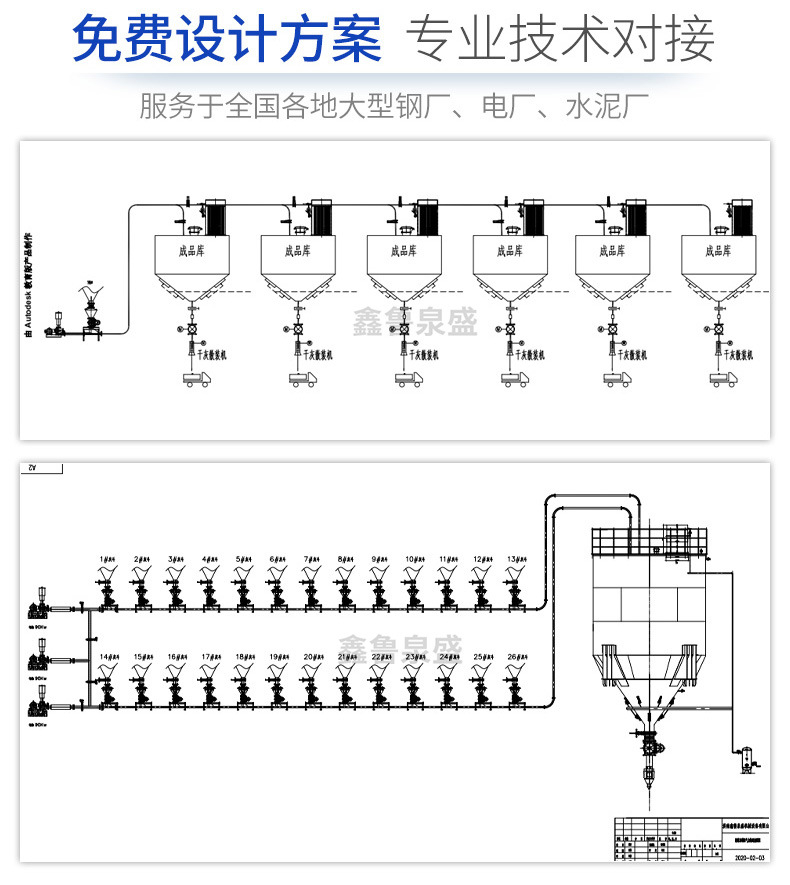
Rotary feeder pneumatic conveying, also known as air flow conveying, utilizes the energy of air flow to transport granular materials along the direction of air flow in a closed pipeline. It is a specific application of fluidization technology. The structure of the pneumatic conveying device is simple, easy to operate, and can be used for horizontal, vertical, or inclined conveying. During the conveying process, it can also perform physical operations such as heating, cooling, drying, and air flow classification, as well as certain chemical operations.
The shaft sealing structure of the rotary feeder requires high requirements. There are two sealing rings at each end of the rotary valve rotor. During normal operation of the equipment, the chamber is filled with gas slightly higher than the conveying pressure to ensure that dust does not enter the rotor end. If dust enters the sealing element, it will increase the friction between the sealing element and the shaft, accelerate the wear of the sealing element and the shaft, and cause the sealing element and the shaft to lose their sealing effect in a short period of time.
 Jinan Xinlu Quansheng Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd
Jinan Xinlu Quansheng Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd